How to Calculate Point Price Elasticity of Demand
When calculating elasticity of demand there are two possible ways.
- Point elasticity of demand takes the elasticity of demand at a particular point on a curve (or between two points)
- Arc elasticity measures elasticity at the midpoint between the two selected points:
Formula for point elasticity of demand is:
PED =
% Δ Q / Q
————-
% Δ P / P
To get more precision, you can use calculus and measure an infinitesimal change in Q and Price ( where ð = very small change) This is the slope of the demand curve at that particular point in time.
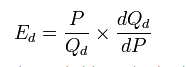
Arc Elasticity
Arc elasticity measures the mid point between the two selected points:
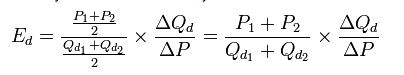
Example of Difference between Point and Arc Elasticity A to B
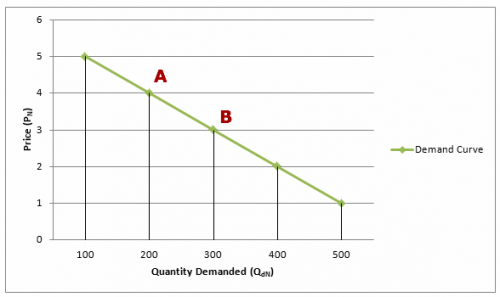
Point elasticity A to B
- Quantity increase from 200 to 300 = 100/200 = 50%
- Price falls from 4 to 3 = 1/4 = -25%
- Therefore PED = 50/ -25 = – 2.0
Mid Point (Arc) Elasticity A to B
- Mid point of Q = (200+300) / 2 = 250
- Mid Point of P = (3+4) / 2 = 3.5
- Q % = (100/250) = 40%
- P % = 1/3.5 = 28.57
- PED = 40/-28.57 = – 1.4
(or ( 3.5/250) * 100/1 = – 1.4)
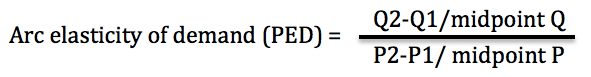
Example of calculating Arc Elasticity of Demand
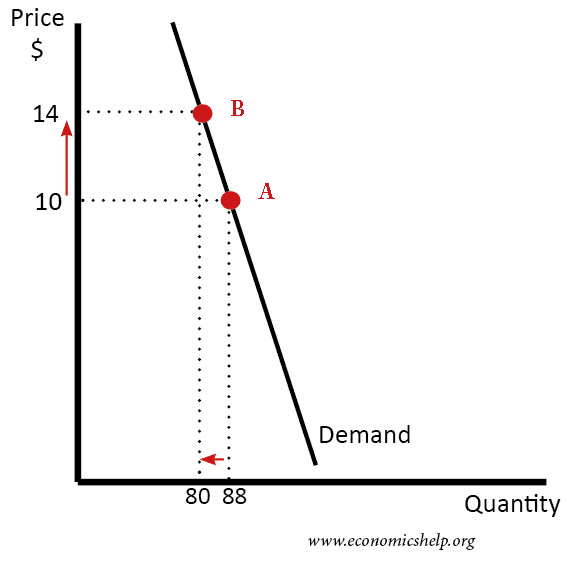
Arc 'mid-point' elasticity
- The mid point of Q = (80+88)/2 = 84
- The mid-point of P =(10+14)/2 =12
- % change in Q = 88-80/84 = -0.09524
- % change in price = (14-10)/12 = 0.3333
- PED = 0.333/-0.9524 = -0.285
Comparison with measuring elasticity as point A to B
If we calculated elasticity from point A to B. We would take the starting point as the reference.
- The % change in Q would be 8/88 = 10%
- The % change in Price would be 4/10 = -40%
- Therefore PED would be 10/-40 = -0.25
Example 2
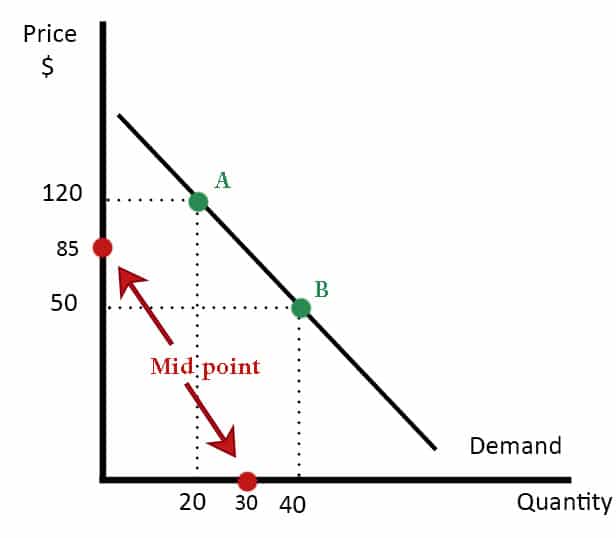
Quantity has fallen from 40 to 20 (change in quantity of 20)
Using arc-elasticity of demand
PED =
Change in Q (20) /midpoint (30) = – 0.66666
Change in p (70) /midpoint (85) = 0.823529
PED = – 0.809
If we calculated PED from points B to A.
% change in QD would be 20/40 (50%
% change in price would be 70/50 (140%)
PED = -0.35
If we calculated PED from points A to B
% change in QD would be 20/20 (100%)
% change in price would be 70/120 (58%)
PED = -1.72
Readers Question: I wonder if you could possibly help with the problem we encountered when we're trying to calculate PED and a change in Total Revenue in a random example.
By taking random numbers we have found ourselves in a situation where TR has not increased when the price increased, given that D was price inelastic.The figures are as follows:
- Price increased from 10-20, (10/10 = 100% increase in price)
- QD had fallen from 10-5 units. (5/10 = 50% fall in price
- Surely, it gives PED of -0.5? – yes using PED
This suggests that D is price inelastic, hence TR should have increased. But it did not. Before the price was raised it equalled: 10×10=100 and after the rise in price: 20×5=100. It remained constant. Could you possibly explain why this has occurred?
All textbooks say that TR should increase when P is raised and D is price inelastic. It should work for any numbers as we can draw a demand curve through these two points (whether a straight line or hyperbolic). Does this imply that if demand is price inelastic and P rises TR may EITHER increase or stay the same or is there a much-complicated answer?
Using Arc elasticity of demand
we get a different elasticity of demand
Firstly we find the midpoint of Q and P. For Q This is (10+20)/2. For P this is 1(0+5)/2 = 7.5
- QD = 10/15 = 66% increase in quantity
- Price = 5/7.5 = 66% fall in price.
Therefore PED = 66/66 = 1.0 This explains why the revenue remained the same.
Elasticity and Revenue
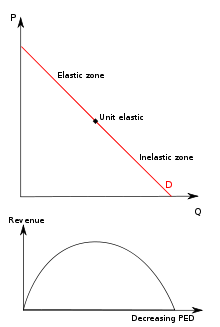
The thing with a straight line is that the elasticity varies. At the top left, quantity is showing a big % increase, compared to price.
Therefore, it makes a big difference whether we use point elasticity of arc elasticity.
Unitary Elasticity
This will be a rectangular hyperbola
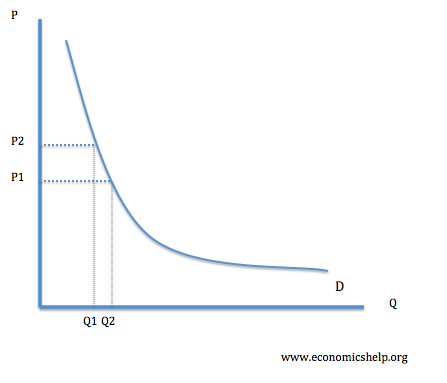
With this shape, the % change is constant.
Note for A Level Students
It is not needed to know the difference between point and arc elasticity. I teach just point elasticity. That is why your calculations were correct. But, outcome confusing.
Related
- Understanding elasticity
How to Calculate Point Price Elasticity of Demand
Source: https://www.economicshelp.org/blog/6260/economics/difference-between-point-and-arc-elasticity-of-demand/